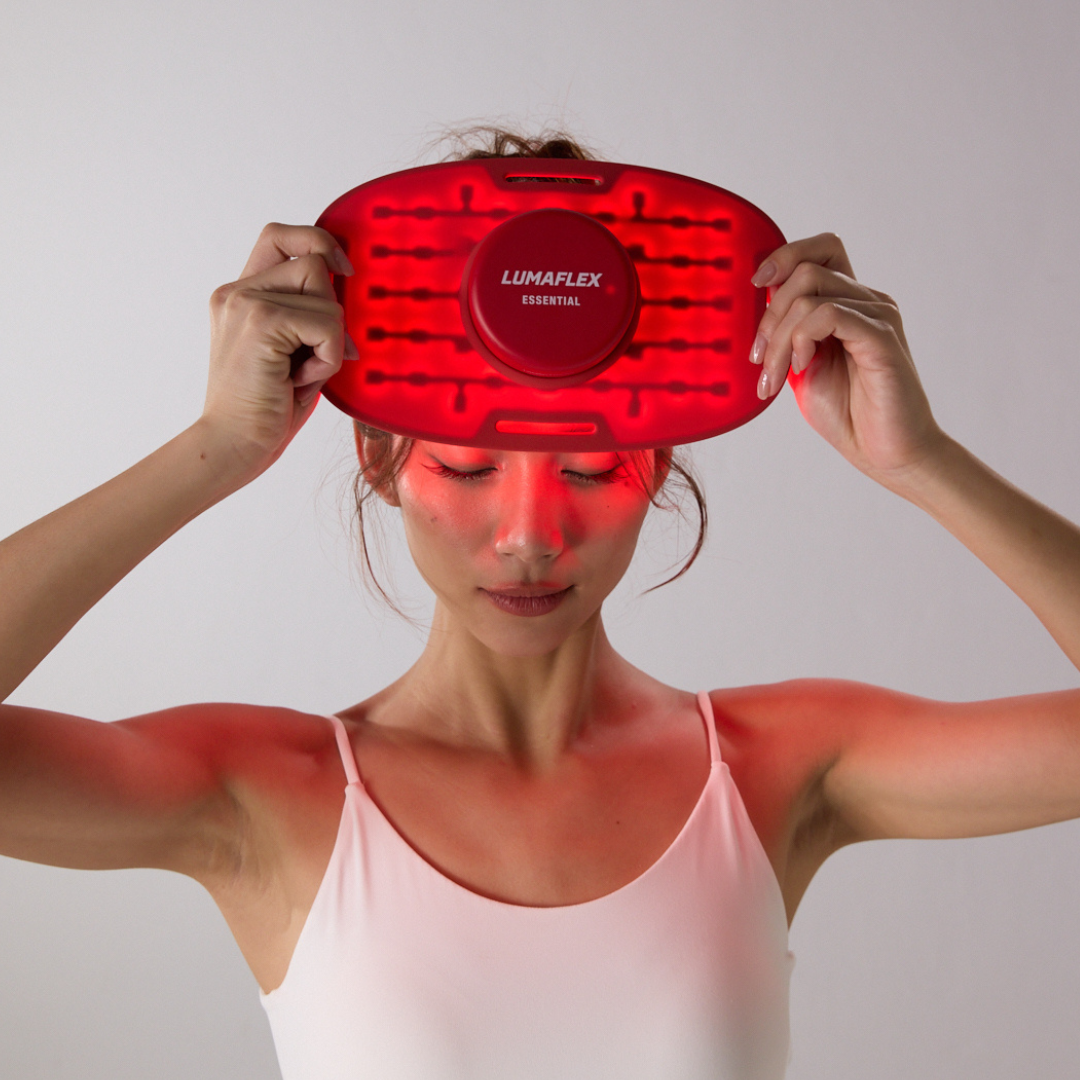
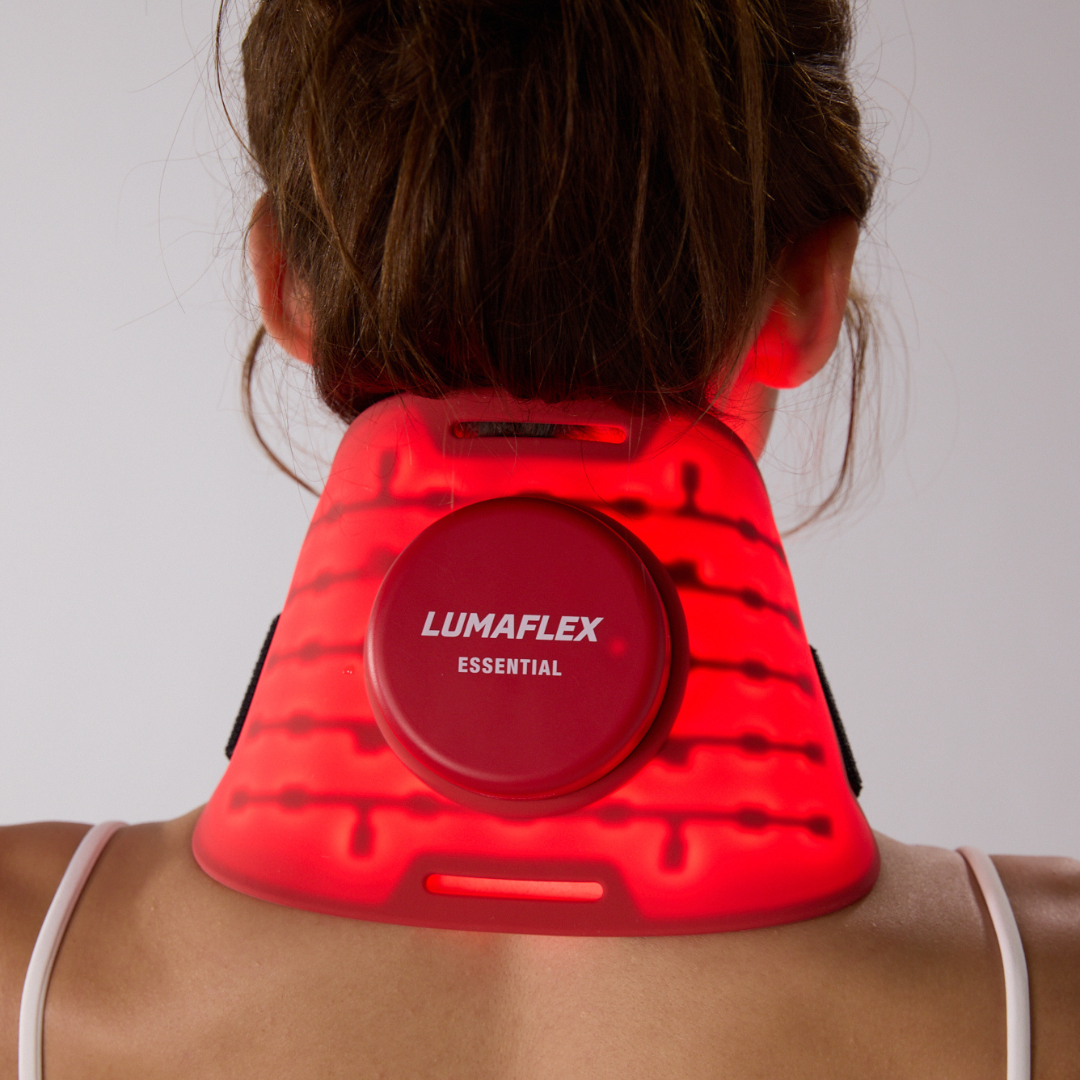
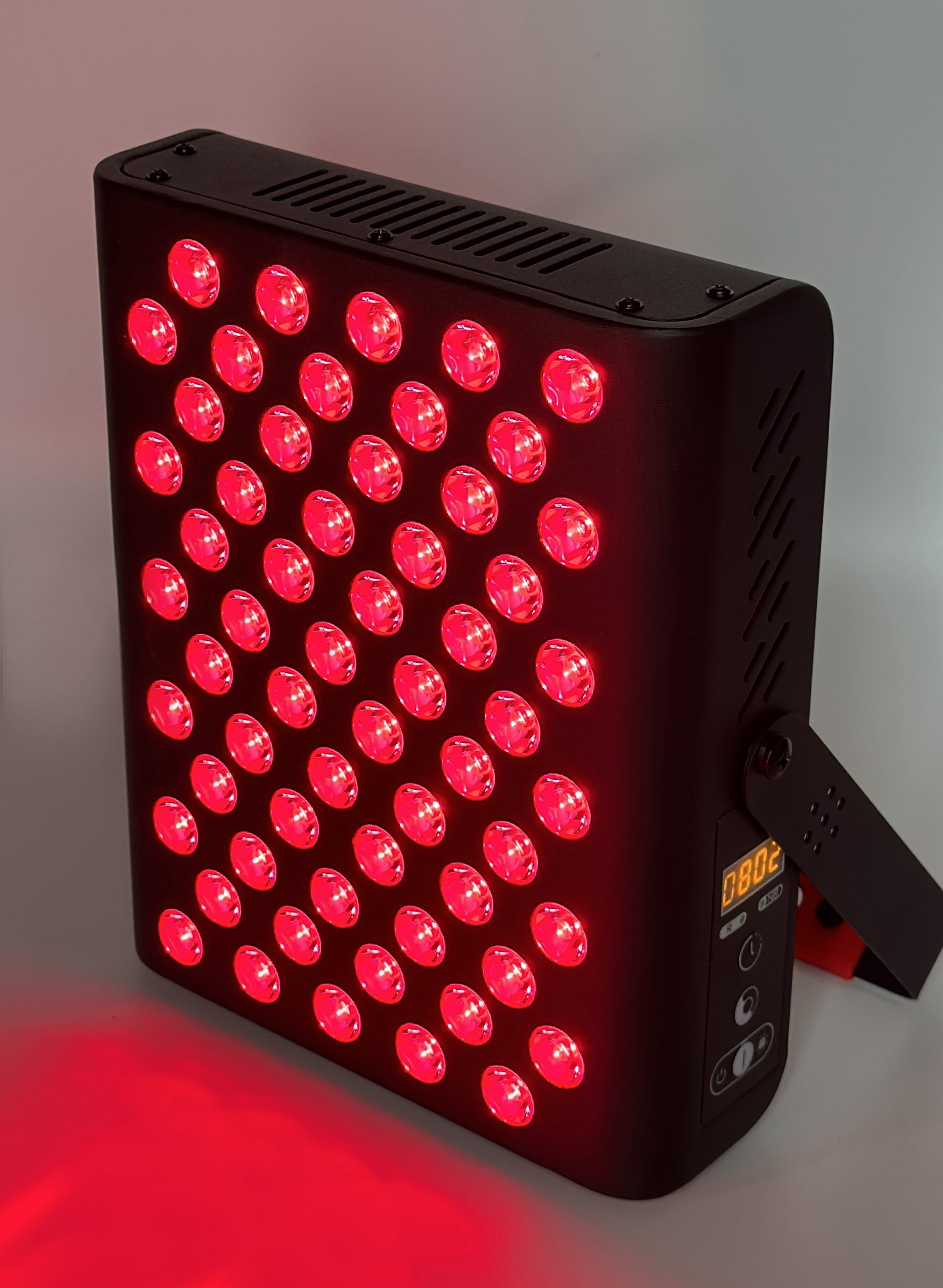
Since the beginning of the new millennium, there has been increasing evidence that different wavelengths of light affect our body’s biochemistry and therefore our well-being. Red (RED) and Near-Infrared (NIR) light are particularly effective. The red spectrum is visible to the eye and is mostly absorbed by the skin. Infrared light is invisible to the human eye. This light penetrates deeper into our bodies (unlike other wavelengths, which are absorbed by the skin), where it has a positive effect on our mitochondria, cells, organs and endocrine glands.
The new science of photobiomodulation has brought us several thousand studies (including human studies) over the past two decades showing that the therapeutic use of red and near-infrared light can keep our bodies healthier on almost every level.
We have divided the effects of RED and NIR therapy into 9 categories and provide an overview of each below. You can also click “more” for more specific information, including selected studies.
- Red light therapy works on mitochondria to increase the production of a key energy source called ATP. (Link)
- Red light therapy can improve muscle function, reduce muscle fatigue during exercise, and improve muscle recovery. This may be beneficial for athletes, people with muscle injuries, and patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. (Reference)
- Red light therapy improves muscle strength, reduces delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS), and reduces levels of biomarkers of muscle damage to a greater extent than cryotherapy. Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that photobiomodulation can improve muscle recovery after high-intensity exercise and is more effective than cryotherapy. (Reference)
- Infrared light used before eccentric training improves hypertrophic response and muscle strength gains in healthy subjects. (Reference)
- The meta-analysis examined time to exhaustion, number of repetitions, isometric peak torque, and blood lactate levels. Positive results were obtained using a wavelength range of 655 to 950 nm. (Reference)
- Photobiomodulation using red and near-infrared light can increase muscle mass gained after training, reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in muscles. (Reference)
- Red and near-infrared light therapy can slow the development of muscle fatigue during exercise, reduce blood lactate levels after exercise, and inhibit the release of inflammatory biomarkers. (Reference)
- Stimulating the quadriceps muscle with near-infrared light (NIR) immediately after leg press and leg extension exercises reduced muscle damage, muscle soreness, and increased muscle mass. (Reference)
- Near-Infrared light therapy (NIR) administered immediately after a leg press exercise increased strength compared to strength training without NIR therapy. The NIR group also had slightly greater increases in thigh circumference. (Reference)
- Red light therapy in elite female basketball players had a positive effect on their endurance. (Link)
- Near-infrared (NIR) light therapy enhances the effects of exercise in obese women who are losing weight. Improvements in lipid profiles and reductions in adipose tissue indicate increased metabolic activity and altered fat metabolism. (Reference)